|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
 - -
|
|

|
Lockheed C-141 StarLifter Heavy Transport |
|
DESCRIPTION:
The C-141 StarLifter was originally designed to meet a US Air Force requirement for a large troop-carrying aircraft with global range. To meet this need, the C-141 could transport up to 154 troops or 123 paratroopers over distances of nearly 3,000 miles. The C-141 was the world's first military transport powered by turbofan engines. The design also featured a high mounted wing to maximize cargo space as well as clamshell doors at the rear fuselage for loading and unloading. Shortly after entering service in 1964, the new C-141 fleet soon proved its usefulness during the conflict in Vietnam. However, the Air Force quickly realized that the C-141 was capable of carrying much greater loads than could physically fit within the aircraft. Lockheed was then contracted to convert some 270 aircraft to the C-141B standard with a fuselage extension and in-flight refueling capability. About 68 of these aircraft were later upgraded with glass cockpit displays and designated as the C-141C. The final years of service for the C-141 proved to be some of the most active for the aircraft, and the StarLifter remained an important component of the US Air Force's transport fleet through 2005. From 2002 until the aircraft's final combat mission in September 2005, the C-141 completed over 2,000 combat sorties and transported more than 70 million pounds of equipment and materials in the Middle East. The C-141 also flew over 70 percent of the aeromedical evacuation flights from the Middle East and Iraq. The final C-141 was retired in May 2006 to go on display at the National Museum of the United States Air Force in Dayton, Ohio. This aircraft, named Hanoi Taxi, had flown the first mission of Operation Homecoming in 1973 to return American prisoners of War from North Vietnam to the US. As the remaining C-141 fleet was retired during the late 1990s and early 2000s, the aircraft was replaced by the C-17 Globemaster III.
Data below for C-141B |
|
| HISTORY: | |
| First Flight |
(YC-141A) 17 December 1963 (YC-141B) 24 March 1977 |
| Service Entry |
(C-141A) 19 October 1964 (C-141B) December 1979 (C-141C) October 1997 |
| Retirement |
(C-141C) 6 May 2006
|
|
CREW:
|
five or six: pilot, co-pilot, two flight engineers, loadmaster (plus navigator for airdrops) aeromedical evacuation crew typically includes two flight nurses and three medical technicians |
| PASSENGERS: |
(C-141A) 154 troops or 123 paratroops (C-141B) 200 troops or 155 paratroops |
|
ESTIMATED COST:
|
(C-141B) $47.4 million [2002$]
|
| AIRFOIL SECTIONS: | |
| Wing Root | NACA 1713-64 |
| Wing Tip |
NACA 29010-94
|
| DIMENSIONS: | |
| Length | 168.29 ft (51.29 m) |
| Wingspan | 159.92 ft (48.74 m) |
| Height | 39.25 ft (11.96 m) |
| Wing Area | 3,220 ft² (299.8 m²) |
|
Canard Area
|
not applicable
|
| WEIGHTS: | |
| Empty |
(C-141A) 133,730 lb (60,680 kg) (C-141B) 148,120 lb (67,185 kg) |
| Normal Takeoff | unknown |
| Max Takeoff |
(C-141A) 316,600 lb (143,600 kg) (C-141B) 343,000 lb (155,585 kg) |
| Fuel Capacity | unknown |
|
Max Payload
|
(C-141A) 70,850 lb (32,135 kg) (C-141B) 90,880 lb (41,220 kg) |
| PROPULSION: | |
| Powerplant | four Pratt & Whitney TF33-7 turbofans |
|
Thrust
|
84,000 lb (374 kN)
|
| PERFORMANCE: | |
| Max Level Speed |
at altitude: 565 mph (910 km/h) at sea level: unknown cruise speed: 555 mph (885 km/h) |
| Initial Climb Rate | 2,920 ft (890 m) / min |
| Service Ceiling | 41,600 ft (12,680 m) |
| Range |
typical: 2,570 nm (4,750 km) ferry: 6,160 nm (11,400 km) [unrefueled] |
| g-Limits |
unknown
|
| ARMAMENT: | |
| Gun | none |
| Stations | none |
| Air-to-Air Missile | none |
| Air-to-Surface Missile | none |
| Bomb | none |
| Other |
none
|
| KNOWN VARIANTS: | |
| YC-141A | Prototype |
| C-141A | First production model; 284 built |
| YC-141B | Prototype of the improved C-141B |
| C-141B | Improved transport with in-flight refueling capability and a fuselage plug increasing length by 23.33 ft (thereby increasing cargo volume by 2,171 cubic ft) allowing an increase from 10 to 13 cargo pallets carried in the hold; 270 converted |
| C-141C |
Update applied to C-141B models fitted with modernized glass cockpit displays; 68 converted
|
| KNOWN COMBAT RECORD: |
Vietnam War (USAF, 1965-1972) Yom Kippur War (USAF, 1973) Panama - Operation Just Cause (USAF, 1989) Iraq - Operation Desert Storm (USAF, 1991) Kosovo - Operation Allied Force (USAF, 1999) Afghanistan - Operation Enduring Freedom (USAF, 2001-2005) Iraq - Operation Iraqi Freedom (USAF, 2003-2005) |
| KNOWN OPERATORS: |
United States (US Air Force)
|
|
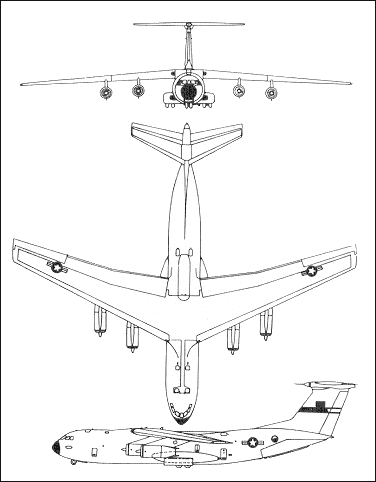
3-VIEW SCHEMATIC:
|
|
SOURCES:
|
|


|
Aircraft | Design | Ask Us | Shop | Search |

|
|
| About Us | Contact Us | Copyright © 1997- | |||
|
|
|||