|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
 - -
 - -
|
|

|
Antonov An-124 Ruslan ASCC codename: Condor Heavy Transport |
|
DESCRIPTION:
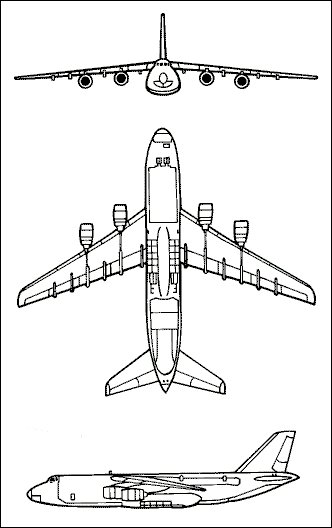
Until the appearance of the related An-225, the Antonov An-124 was the largest aircraft in the world, narrowly beating out the similar C-5 Galaxy. The An-124 built on experience with the giant An-22 turboprop but added several improvements to make the Ruslan more effective. The An-124 is equipped with an upward-hinging nose and a tail ramp for true roll-on roll-off loading capability. In addition, the two sets of nose wheels can be retracted on the ground to lower the nose and ease cargo loading. The An-124 design also features full-span leading-edge slats on a swept wing allowing excellent short-takeoff ability for such a large plane. The landing gear also feature 24 wheels so that the An-124 can operate from rough fields. A large compartment for up to 88 passengers is provided aft of the flight deck in addition to the 118 ft x 21 ft x 14.5 ft main cargo deck for a total volume of 44,725 ft³. The An-124 first entered commercial service with Aeroflot and was used primarily to transport outsize cargo. Many of these aircraft are now available for leasing by Western companies. A number of An-124 aircraft were also acquired by the Russian military for strategic transport duties. A total of 54 An-124 aircraft were built from 1984 to 1997. By 2000, 26 were in service with the Russian Air Force and 21 with civil operators while five had been lost in accidents. Budget restraints prevented any further military sales but production for commercial customers was continuing at the rate of about four planes per year until about 2003. Although manufacturing had been stopped, Russia and Ukraine have agreed to restart the production line in the second half of 2008 if enough orders are placed.
Last modified 17 March 2011
|
|
| HISTORY: | |
| First Flight | 26 December 1982 |
|
Service Entry
|
1987
|
| CREW: |
six: pilot, co-pilot, navigator, communication operator, engineer, electrical engineer military models also carry a loadmaster up to twelve cargo handlers and a second primary crew for long flights may also be carried |
| PASSENGERS: |
88
|
|
ESTIMATED COST:
|
$150 to $160 million [2008$]
|
| AIRFOIL SECTIONS: | |
| Wing Root | unknown supercritical |
|
Wing Tip
|
unknown supercritical
|
| DIMENSIONS: | |
| Length | 226.46 ft (69.10 m) |
| Wingspan | 240.48 ft (73.30 m) |
| Height | 69.10 ft (21.08 m) |
| Wing Area | 6,760 ft² (628.0 m²) |
|
Canard Area
|
not applicable
|
| WEIGHTS: | |
| Empty | 385,810 lb (175,000 kg) |
| Normal Takeoff | 864,210 lb (392,000 kg) |
| Max Takeoff | 892,870 lb (405,000 kg) |
| Fuel Capacity |
(An-124) 471,215 lb (213,740 kg) (An-124-100) 468,150 lb (212,350 kg) |
|
Max Payload
|
330,695 lb (150,000 kg)
|
| PROPULSION: | |
| Powerplant | four Loratev D-18T turbofans |
| Thrust |
206,360 lb (918.0 kN)
|
| PERFORMANCE: | |
| Max Level Speed |
at altitude: 530 mph (850 km/h) at 25,000 ft (7,620 m), Mach 0.77 at sea level: unknown cruise speed: 465 mph (750 km/h) |
| Initial Climb Rate | unknown |
| Service Ceiling | 39,335 ft (12,000 m) |
| Range |
2,430 nm (4,500 km) with 330,695 lb (150,000 kg) payload 6,480 nm (12,000 km) with 88,185 lb (40,000 kg) payload ferry: 8,690 nm (16,090 km) |
| Endurance | 20 hr |
| g-Limits |
unknown
|
| ARMAMENT: | |
| Gun | none |
| Stations | none |
| Air-to-Air Missile | none |
| Air-to-Surface Missile | none |
| Bomb | none |
|
Other
|
none
|
| KNOWN VARIANTS: | |
| An-124 | Military transport model |
| An-124A | Proposed military version that would have used six sets of tandem wheels on the main gear instead of five to permit operations from rougher airfields |
| An-124-100 | Civil version modified for compatibility with cargo loading infrastructure at commercial airports |
| An-124-100M | Improved model equipped with uprated D-18 Series 3 engines allowing greater range and shorter takeoff distance, also fitted with more advanced Western avionics allowing crew size to be reduced from 6 to 4 by eliminating the communication operator and engineer |
| An-124-100V | An-124-100 aircraft modified with noise-reduction covers on the engine nacelles to meet noise pollution standards |
| An-124-100MV | Model incorporating the improvements of both the An-124-100M and An-124-100V versions |
| An-124-100M-150 | Upgrade for An-124-100M models to increase payload and maximum takeoff weight, extend flight hours from the original 7,500 to 24,000 (and ultimately 40,000), and replace outdated equipment |
| An-124-102 | Proposed model with a three-crew cockpit |
| An-124-130 | Proposed model, details unknown |
| An-124-200 | Proposed upgrade to add General Electric CF6-80C2 turbofan engines to the An-124-100M |
| An-124-210 | Similar to the An-124-100M but to be equipped with Rolls-Royce RB211-52H-T engines as well as new avionics |
| An-124AK | Proposed launch platform for the Shtil-3A ballistic missile used for launching satellites into orbit, the missile would be carried in the main cargo hold to an altitude of 36,090 ft (11,000 m) and deployed through the aft cargo doors using a parachute before its motor ignited |
| An-124FFR | Proposed firefighting model capable of carrying over 440,000 lb (200,000 kg) of water or fire retardant |
| An-124KC | Aerial refueling tanker proposed to the US as a replacement for the KC-135 |
| An-122KC |
Believed to be a twin-engine version of the An-124 aerial refueling tanker offered to the US Air Force but
few details are known
|
|
KNOWN COMBAT RECORD:
|
none
|
| KNOWN OPERATORS: | |
| Civil |
Aeroflot Air Foyle AJAX Antonov Airlines Antonov AirTrack Atlant Soyuz Airlines HeavyLift Cargo Airlines Libyan Arab Air Cargo Maximus Air Cargo Russian State Transport Company Titan Cargo Transaero Airlines TransCharter Titan Cargo Volga-Dnepr Airlines Polet Airlines Rossiya |
| Military |
Russia, Voyenno Vozdushniye Sili (Russian Air Force) Ukraine, Viys'kovo-Povitriani Syly Ukrayiny (Ukraine Military Air Forces) Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, Voyenno Vozdushniye Sili (Soviet Air Force) |
|
3-VIEW SCHEMATIC:
|
|
SOURCES:
|
|


|
Aircraft | Design | Ask Us | Shop | Search |

|
|
| About Us | Contact Us | Copyright © 1997- | |||
|
|
|||