|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
 - -
|
|

|
de Havilland Comet Long-Range Jetliner |
|
DESCRIPTION:
Certainly one of the most tragic stories of the jet age revolves around the unfortunate de Havilland Comet. Building on the British lead in jet engine technology following World War II, de Havilland developed and flew the first commercial jet aircraft in 1949, several years ahead of rival Boeing in America. Known as the D.H.106 Comet, the ailiner used four of the new de Havilland Ghost 50 turbojet engines mounted in the wing root leading edge of an otherwise fairly typical commercial airliner of the day. Because it represented such a revolutionary advance in commercial travel, the Comet was put through an extensive series of test flights and certifications over the next three years. These 500 hours worth of flight crew training and proving flights included long overseas flights, tropical operations, and high altitude takeoffs. Having successfully completed these tests with no apparent difficulties, launch customer BOAC received permission to begin commercial operations in early 1952. The first hint of trouble with the design came exactly one year later when a Comet mysteriously crashed shortly after takeoff on 2 May 1953. Two similar crashes in early 1954 forced British authorities to ground the entire fleet pending investigation. Over the following months, extensive tests were performed on the aircraft to determine what could have caused these mysterious accidents. The answer finally came after a fuselage had been submerged in a tank of water and repeatedly pressurized and depressurized to represent repeated flight cycles. After several thousand of these cycles, fatigue cracks were found to be spreading from the square edges of the windows in the passenger cabin. These cracks would eventually reach a critical size where they would grow rapidly resulting in a catastrophic depressurization that would destroy an aircraft in flight. All Comets then in service or under construction were either scrapped or modified with rounded-corner windows to correct the fatugue problem. Nevertheless, it took four years for the aircraft to be recertified for commercial service. By this time, the much improved Comet 4 series was available, equipped with better engines, greater fuel capacity for increased range, and a lengthened cabin for additional passengers. However, the four year hiatus in Comet operations had driven most prospective customers to the rival Boeing 707 and Douglas DC-8. These designs soon claimed the bulk of the market. Only about 90 Comets ever reached commercial operators, and most were removed from service by the early 1980s. A few additional aircraft were used by the military, but only the Nimrod, a Comet derivative, remains in use. Had the Comet not been plagued by a fatal design flaw, Britain might well still dominate commercial aviation today.
Last modified 27 September 2009
|
|
| HISTORY: | |
| First Flight |
(Comet 1) 27 July 1949 (Comet 1A) 11 August 1952 (Comet 2) 27 August 1953 (Comet 3) 19 July 1954 (Comet 4) 27 April 1958 (Comet 4B) 27 June 1959 (Comet 4C) 31 October 1959 |
|
Service Entry
|
(Comet 1) 22 January 1952 (freight service with BOAC) (Comet 1) 2 May 1952 (passenger service with BOAC) (Comet 4) 4 October 1958 |
| CREW: |
four flight crew
|
| PASSENGERS: |
(Comet 1) 36 in three classes (Comet 1A) 44 in three classes (Comet 2) 44 in three classes (Comet 3) 58 in three classes, 78 in two classes (Comet 4) 56 in three classes, 81 in two classes, 109 in one class (Comet 4B) 71 in three classes, 101 in two classes, 119 in one class (Comet 4C) 79 in three classes, 101 in two classes, 119 in one class |
|
ESTIMATED COST:
|
(Comet 1) £250,000
|
| AIRFOIL SECTIONS: | |
| Wing Root | unknown |
|
Wing Tip
|
unknown
|
| DIMENSIONS: | |
| Length |
(Comet 1) 93.78 ft (28.61 m) (Comet 1A) 93.78 ft (28.61 m) (Comet 2) 96.79 ft (29.53 m) (Comet 3) 111.50 ft (33.98 m) (Comet 4) 111.50 ft (33.98 m) (Comet 4B) 117.90 ft (35.97 m) (Comet 4C) 117.90 ft (35.97 m) |
| Wingspan |
(Comet 1) 114.83 ft (34.98 m) (Comet 1A) 114.83 ft (34.98 m) (Comet 2) 114.83 ft (34.98 m) (Comet 3) 114.83 ft (34.98 m) (Comet 4) 114.83 ft (34.98 m) (Comet 4B) 107.83 ft (32.87 m) (Comet 4C) 114.83 ft (34.98 m) |
| Height | 29.50 ft (8.99 m) |
| Wing Area |
(Comet 1) 2,023 ft² (188.30 m²) (Comet 1A) 2,023 ft² (188.30 m²) (Comet 2) 2,023 ft² (188.30 m²) (Comet 3) 2,121 ft² (197.04 m²) (Comet 4) 2,121 ft² (197.04 m²) (Comet 4B) 2,055 ft² (191.30 m²) (Comet 4C) 2,121 ft² (197.04 m²) |
|
Canard Area
|
not applicable
|
| WEIGHTS: | |
| Empty |
(Comet 4) 75,425 lb (34,210 kg) (Comet 4B) 78,350 lb (35,540 kg) (Comet 4C) 79,610 lb (36,110 kg) |
| Normal Takeoff | unknown |
| Max Takeoff |
(Comet 1) 104,985 lb (47,620 kg) (Comet 1A) 115,000 lb (52,160 kg) (Comet 2) 120,000 lb (54,430 kg) (Comet 3) 144,975 lb (65,760 kg) (Comet 4) 162,000 lb (73,480 kg) (Comet 4B) 157,875 lb (71,610 kg) (Comet 4C) 162,000 lb (73,480 kg) |
| Fuel Capacity |
(Comet 1) 7,045 gal (27,300 L) (Comet 1A) 8,100 gal (31,395 L) (Comet 2) 8,100 gal (31,395 L) (Comet 3) 9,805 gal (38,000 L) (Comet 4) 10,440 gal (40,450 L) (Comet 4B) 9,150 gal (35,460 L) (Comet 4C) 10,440 gal (40,450 L) |
|
Max Payload
|
(Comet 1) 12,500 lb (5,670 kg) (Comet 1A) 11,800 lb (5,350 kg) (Comet 2) 13,500 lb (6,125 kg) (Comet 3) 20,200 lb (9,160 kg) (Comet 4) 20,280 lb (9,200 kg) (Comet 4B) 24,100 lb (10,930 kg) (Comet 4C) 24,100 lb (10,930 kg) |
| PROPULSION: | |
| Powerplant |
(Comet 1) four de Havilland Ghost 50 Mk 1 turbojets (Comet 1A) four de Havilland Ghost 50 Mk 2 turbojets (Comet 2) four Rolls Royce Avon 503 turbojets (Comet 3) four Rolls Royce Avon 523 turbojets (Comet 4) four Rolls Royce Avon 524 turbojets (Comet 4B) four Rolls Royce Avon 525B turbojets (Comet 4C) four Rolls Royce Avon 525B turbojets |
| Thrust |
(Comet 1) 20,050 lb (89.2 kN) (Comet 1A) 20,050 lb (89.2 kN) (Comet 2) 29,225 lb (130 kN) (Comet 3) 40,000 lb (178 kN) (Comet 4) 42,000 lb (187 kN) (Comet 4B) 42,000 lb (187 kN) (Comet 4C) 42,000 lb (187 kN) |
| PERFORMANCE: | |
| Max Level Speed |
cruise speed: (Comet 1) 450 mph (725 km/h) (Comet 1A) 450 mph (725 km/h) (Comet 2) 480 mph (770 km/h) (Comet 3) 500 mph (805 km/h) (Comet 4) 500 mph (805 km/h) (Comet 4B) 525 mph (850 km/h) (Comet 4C) 500 mph (805 km/h) |
| Initial Climb Rate | unknown |
| Service Ceiling |
(Comet 1) 42,000 ft (12,800 m) (Comet 1A) 42,000 ft (12,800 m) (Comet 2) 42,000 ft (12,800 m) (Comet 3) 40,000 ft (12,200 m) (Comet 4) 40,000 ft (12,200 m) (Comet 4B) 37,700 ft (11,500 m) (Comet 4C) 39,000 ft (11,900 m) |
| Range |
(Comet 1) 1,300 nm (2,415 km) (Comet 1A) 1,535 nm (2,850 km) (Comet 2) 2,195 nm (4,065 km) (Comet 3) 2,345 nm (4,345 km) (Comet 4) 2,800 nm (5,190 km) (Comet 4B) 2,170 nm (4,025 km) (Comet 4C) 3,725 nm (6,900 km) |
| g-Limits |
unknown
|
| KNOWN VARIANTS: | |
| G-5-1 and G-5-2 | Two prototypes originally equipped with single-wheel main landing gear, G-5-1 later modified with 4-wheel gear; prototypes also modifed to test drooped leading edges and rocket assisted takeoffs |
| Comet 1 | First production model and first aircraft to initiate commercial jet passenger sevice, entire Comet fleet grounded following crash of five of these models leading to discovery of structural failure of the passenger cabin; 9 built (5 crashed) |
| Comet 1A | Similar to Comet 1 but with increased fuel capacity and reinforced structure for greater takeoff weight; 10 built (3 crashed) |
| Comet 1XB | Comet 1A aircraft modified with stronger structure and oval windows to correct problems with earlier models; 4 converted |
| Comet 2X | Developmental aircraft converted from a Comet 1 airframe and used to test new engines and other features for Comet 2; 1 converted |
| Comet 2 | Enlarged model with stretched fuselage for increased passenger load and larger fuel capacity, ordered by commercial operators but never entered service because of Comet 1 crashes; 22 built but 5 scrapped, 3 put into storage, and remainder converted into following variants primarily used by the RAF |
| Comet C.2 | Cargo transport converted from aborted Comet 2 airframes with reinforced fuselage and cabin floor, used by RAF; 8 converted |
| Comet T.2 | Crew trainers converted from aborted Comet 2 airframes for RAF; 2 converted |
| Comet 2E | Comet 2 airframes modified with new engines and used to test equipment for Comet 4; 2 converted |
| Comet 2R | Comet 2 airframes fitted with special electronics in an unpressurized fuselage, used by the RAF; 3 converted |
| Comet 3 | Developmental model with lengthened fuselage for more passengers and fuel but project cancelled following Comet 1 accidents, leter used as prototype for Comet 4B; 1 built and 10 others scrapped |
| Comet 4 | First variant certified for passenger operations following Comet 1 disaster, similar to Comet 3; 28 built |
| Comet 4A | Short range version of Comet 4 with lengthened fuselage and reduced wingspan, order from Capital Airlines cancelled and did not enter production; none built |
| Comet 4B | Short range version of Comet 4 similar to Comet 4A but with even longer fuselage and new engine; 18 built |
| Comet 4C | Final production model, combined lengthened fuselage of Comet 4B with wing of Comet 4 for greater passenger load over standard ranges; 23 built |
| Comet C.4 | Transport variant of Comet 4C used by RAF; 5 built |
| Comet 5 | Proposed new model to compete with DC-8 and Boeing 707, not built |
| Nimrod |
Maritime reconnaissance aircraft developed from basic Comet 4C airframe
|
| KNOWN OPERATORS: | |
| Civil |
Aerolineas Argentinas Air France Air India BOAC British Commonwealth Pacific British European Airways Canadian Pacific Airlines Channel Airways Dan-Air London East African Airlines Japan Air Lines King Ibn Saud of Saudi Arabia Kuwait Airways LAV Malaysia Singapore Mexicana Airlines Middle East Airlines Misrair Olympic Airways Panair do Brasil Royal Aircraft Establishment Sudan Airways Union Aeromaritime de Transport United Arab Airlines |
| Government/Military |
Canada (Royal Canadian Air Force) United Kingdom (Ministry of Aviation) United Kingdom (Royal Air Force) |
|
3-VIEW SCHEMATIC:
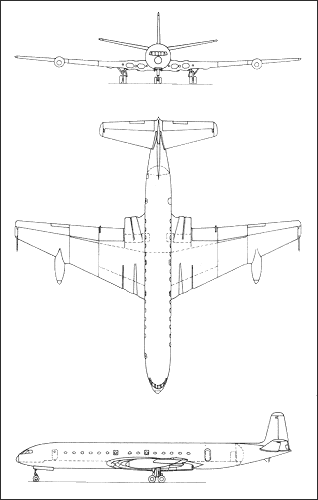
|
|
SOURCES:
|
|


|
Aircraft | Design | Ask Us | Shop | Search |

|
|
| About Us | Contact Us | Copyright © 1997- | |||
|
|
|||