|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
 - -
 - -
|
|

|
Mikoyan Gurevich MiG-29 ASCC codename: Fulcrum Multi-Role Fighter |
|
DESCRIPTION:
The MiG-29 was designed as a replacement for the MiG-21, MiG-23, Su-15 and Su-17 fighters. While its overall appearance is similar to that of the American F/A-18 Hornet, the MiG-29 incorporates much larger and deeper leading-edge root extensions (LERX) for good maneuverability at high angles of attack. A series of auxiliary intakes are mounted on the upper surface of the LERXs allowing the engines to draw in air when the two main inlets are closed. These features are used during ground taxiing to prevent debris from being sucked into the engines. The large nose of the MiG-29 houses a single-seat cockpit for the pilot as well as a large pulse-Doppler look-down/shoot-down radar, laser rangefinder, infrared seeker/tracker system, and a helmet-mounted target-designation system. Though initial production models were not equipped with a fly-by-wire control system, the MiG-29 Fulcrum has shown exceptional agility that has earned great admiration in the West. The MiG-29S model was upgraded with new avionics moved to the upper part of an enlarged fuselage. This modification allows a greater fuel capacity. One of the most advanced variants is the MiG-29M that includes a fly-by-wire control system and a more advanced HUD plus glass-cockpit displays. This model also disposes of the auxiliary engine intakes on the earlier models to make room for additional fuel, short range being the primary disadvantage of initial variants. The Soviet Navy also considered deploying the MiG-29 aboard its Kuznetsov class aircraft carrier, and a navalized MiG-29K was developed and tested. However, the Su-33 was eventually chosen instead. India, however, has purchased a variant of the MiG-29K to be carried aboard a former Russian aircraft carrier being converted for the Indian Navy.
Last modified 05 March 2011
|
|
| HISTORY: | |
| First Flight |
(MiG-29) 6 October 1977 (MiG-29M) 1989 (MiG-29UBT) 8 October 1998 |
|
Service Entry
|
1983
|
| CREW: |
one: pilot
|
|
ESTIMATED COST:
|
unknown
|
| AIRFOIL SECTIONS: | |
| Wing Root | unknown |
|
Wing Tip
|
unknown
|
| DIMENSIONS: | |
| Length | 56.83 ft (17.32 m) |
| Wingspan | 37.29 ft (11.36 m) |
| Height | 15.54 ft (4.73 m) |
| Wing Area | 408 ft² (38.0 m²) |
|
Canard Area
|
not applicable
|
| WEIGHTS: | |
| Empty | 24,030 lb (10,900 kg) |
| Normal Takeoff | 33,600 lb (15,240 kg) |
| Max Takeoff | 40,785 lb (18,500 kg) |
| Fuel Capacity |
internal: unknown external: unknown |
|
Max Payload
|
6,614 lb (3,000 kg)
|
| PROPULSION: | |
| Powerplant |
(MiG-29A) two Klimov/ Sarkisov RD-33 afterburning turbofans (MiG-29M) two Klimov/ Sarkisov RD-33K afterburning turbofans |
| Thrust |
(RD-33) 36,600 lb (162.8 kN) (RD-33K) 41,450 lb (184.44 kN) |
| PERFORMANCE: | |
| Max Level Speed |
at altitude: 1,520 mph (2,445 km/h) at 36,090 ft (11,000 m), Mach 2.3 at sea level: 805 mph (1,200 km/h), Mach 1.06 |
| Initial Climb Rate | 65,000 ft (19,800 m) / min |
| Service Ceiling | 60,700 ft (18,500 m) |
| Range |
typical: 810 nm (1,500 km) 340 nm (630 km) with max payload ferry: 1,570 nm (2,900 km) |
| g-Limits |
unknown
|
| ARMAMENT: | |
| Gun | one 30-mm GSh-301 cannon (150 rds) |
| Stations |
six or seven external hardpoints (MiG-29K) nine external hardpoints (MiG-29M) eight external hardpoints |
| Air-to-Air Missile | R-60/AA-8 Aphid, R-27/AA-10 Alamo, R-73/AA-11 Archer, R-77/AA-12 Adder |
| Air-to-Surface Missile | AS-12, AS-14, AS-17 |
| Bomb | free-fall, guided, cluster bombs |
| Other |
rocket pods, ECM pods, munitions dispensers
|
| KNOWN VARIANTS: | |
| 9-01 | Pre-production model |
| MiG-29 'Fulcrum-A' | First production model, prototypes included three slightly different models with varying types of nose gear, fin, and rudder arrangements |
| MiG-29UB 'Fulcrum-B' | Two-seat trainer with radar removed |
| MiG-29S 'Fulcrum-C' | Improved single-seat fighter for serial production with an enlarged fuselage, new avionics, and a larger fuel capacity |
| MiG-29KVP | MiG-29K prototype built to test catapult takeoff and arrestor gear systems, may also have been used as a trainer for the MiG-29K |
| MiG-29K 'Fulcrum-D' | Navalized one-seat multipurpose fighter for use on aircraft carriers; Russian production cancelled after trials completed but a derivative was later purchased by India |
| MiG-29KU | Trainer version of the MiG-29K with a modified nose adding a separate cockpit for the instructor forward and below the normal cockpit; cancelled |
| MiG-29KUB | Trainer version of the MiG-29K purchased by India and the Russian Navy |
| MiG-29B | Two-seat version, details unknown |
| MiG-29UBT | Two-seat strike model designed for special operations |
| MiG-29SD | Export version of the MiG-29S |
| MiG-29SE | Export version of the MiG-29S with a new ECM jammer |
| MiG-29N | Export version for Malaysia similar to the MiG-29SD and optimized for air defense but equipped with in-flight refueling capability, updated communications equipment, improved navigation systems, and updated engines |
| MiG-29UBN | Two-seat trainer exported to Malaysia |
| MiG-29SM | Improved MiG-29S/SE with in-flight refueling capability, increased payload, and the ability to carry improved air-to-air missiles plus a TV display compatible with the KAB-500KR guided bomb or the Kh-29T missile, also capable of carrying the Kh-31A and Kh-31P missiles |
| MiG-29SMT | Modernization program for MiG-29SM export models with an improved cockpit, improved avionics, and increased range |
| MiG-29SMT-2 | "Second stage" modernization program for export models that provides a new radar, improved engines, revised ECM equipment, a digital fly-by-wire control system, and compatibility with numerous adbanced air-to-air and air-to-surface weapons |
| MiG-29SMTK | Carrier-based export model offered to India, includes folding wings, arrestor gear, and improved navigation systems |
| MiG-29M 'Fulcrum-E' | Improved fighter with fly-by-wire controls, upgraded engines, a modified tail and wing layout, a revised canopy, and the ability to carry guided-munitions |
| MiG-29MaE or MiG-29MEh or MiG-29EM | Export version of the MiG-29M |
| MiG-29MR | Reconnaissance version of the MiG-29M |
| MiG-29UM | Two-seat combat-capable trainer version of the MiG-29M |
| MiG-29M2 'Fulcrum-F' | Two-seat variant of the MiG-29M |
| MiG-29 'Fulcrum-Plus' | MiG-29 variant equipped with thrust-vectoring nozzles and canards, not believed to have been completed or flown due to financial problems |
| MiG-29OVT | Early designation for the MiG-35 |
| MiG-29AS | Upgrade program for single-seat MiG-29 fighters used by Slovakia that includes installation of new IFF equipment and American radios while also adding an improved navigation system; 10 converted |
| MiG-29UBS | Upgrade program for MiG-29UB trainers used by Slovakia; 2 converted |
| MiG-33 | Believed to be a designation for an export version of the MiG-29M |
| MiG-35 |
Upgraded model based on the MiG-29M2 primarily for the export market
|
|
KNOWN COMBAT RECORD:
|
Iraq - Operation Desert Storm (Iraq, 1991) Croatian War of Independence (Yugoslavia, 1991-1995) Chechnya (Russia, 1994-present) Bosnian War (Yugoslavia, 1992-1995) Kosovo - Operation Allied Force (Serbia, 1999) |
|
KNOWN OPERATORS:
|
Algeria, Al Quwwat al Jawwawiya al Jaza'eriya (Algerian Air Force) Angola, Força Aérea Popular de Angola (Angolan People's Air Force) Armenia (Armenian Air Force) Azerbaijan (Azerbaijan Air Force) Bangladesh, Bangladesh Biman Bahini (Bangladeshi Defense Force Air Wing) Belarus, Voyenno Vozdushnyye Sily (Belarus Air Force) Bulgaria, Bulgarski Voenno Vozdushni Sili (Bulgarian Air Defense Force Military Aviation) Croatia, Hrvatske Zracne Snage (Croatian Air Force) Cuba, Defensa Antiaerea y Fuerza Aérea Revolucionaria (Anti-Aircraft Defense and Revolutionary Air Force) Czechoslovakia, Ceskoslovenske Letectvo (Czechoslovak Air Force) Czech Republic, Cesk Letectvo a Protivzbusna Obrana (Czech Air Force and Air Defense) East Germany, Luftstreitkräfte/Luftverteidigung (Air Force/Air Defense Force) Germany, Deutsche Luftwaffe (German Air Force) Hungary, Magyar Légierö (Hungarian Red Air Arm) Hungary, Magyar Honvedseg Repülö Csapatai (Hungarian Air Defense Group) India, Bharatiya Vayu Sena (Indian Air Force) India (Indian Naval Air Squadron) Iran (Islamic Republic of Iran Air Force) Iraq, Al Quwwat Al Jawwiya al Iraqiya (Iraqi Air Force) Kazakhstan (Kazakhstan Air Force) Malaysia, Tentera Udara Diraja Malaysia (Royal Malaysian Air Force) Moldova (Moldovan Air Force) Myanmar, Tamdaw Lay (Myanmar Armed Forces) North Korea (Korean People's Army Air Force) Peru, Fuerza Aérea del Perú (Peruvian Air Force) Poland, Sily Powietrzne Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej (Polish Air Force) Poland, Polska Wojska Lotnicze i Obrony Powietrznej (Polish Air Defense and Aviation Force) Romania, Fortele Aeriene Române (Romanian Air Force) Russia, Voyenno Vozdushniye Sili (Russian Air Force) Russia, Aviatsiya Voyenno-Morskoyo Flota Sily Rossii (Russian Naval Aviation) Serbia, Vazduhoplovstvo i PVO Vojske Srbije (Serbian Air Force) Slovakia, Velitelstvo Vzdusnych Sil (Slovak Air Force) Sri Lanka (Sri Lankan National Air Force) Sudan, Silakh al Jawwiya As'Sudaniya (Sudanese Air Force) Syria, Al Quwwat al-Jawwiya al Arabiya as-Souriya (Syrian Air Force) Turkmenistan, Voyenno-Vozdushneyye Sily (Turkmenistan Air Force) Ukraine, Viys'kovo-Povitriani Syly Ukrayiny (Ukraine Military Air Forces) Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, Voyenno Vozdushniye Sili (Soviet Air Force) Uzbekistan (Uzbek Air Force) Yemen, Al Quwwat al Jawwiya al Yemeniya (Unified Yemen Air Force) Yugoslavia, Ratno Vazduhoplovstvo i Protiv Vazdusna Odbrana (Serbia and Montenegro Air and Air Defence Force) |
|
3-VIEW SCHEMATIC:
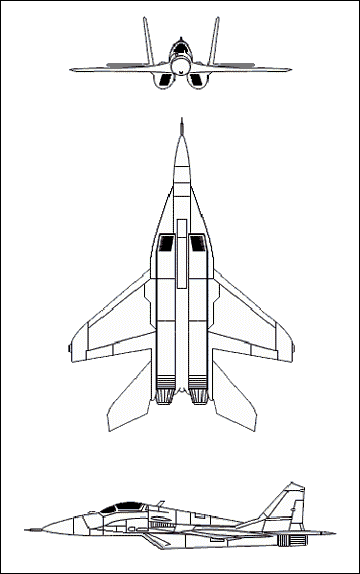
|
|
SOURCES:
|
|


|
Aircraft | Design | Ask Us | Shop | Search |

|
|
| About Us | Contact Us | Copyright © 1997- | |||
|
|
|||