|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
 - -
|
|

|
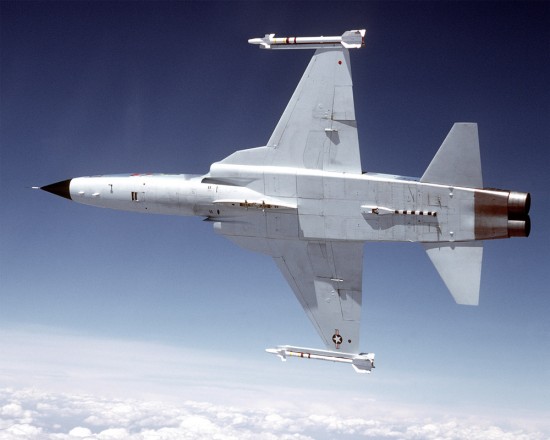
Northrop F-5A Freedom Fighter F-5E Tiger II F-20 Tigershark Light Tactical Fighter |
|
DESCRIPTION:
Northrop began its light fighter project in 1953 that led to a company-financed supersonic trainer called the N-156F Freedom Fighter. Though not purchased by the US military, the government supported the sale of 879 F-5A's to 21 friendly nations. Another 320 aircraft were built under license in foreign countries. The F-5E Tiger II appeared in the early 1970s with more powerful engines, greater fuel capacity, and aerodynamic improvements. Over 1,400 of the Tigers were sold, including some purchased by the US Navy and Air Force for use in the Top Gun and Aggressor programs to simulate enemy aircraft and tactics. A further development of the F-5 was the F-20 Tigershark, similar in performance to the F-16. However, the Tigershark failed to attract a buyer in the competitive fighter market of the late 1980s. Nonetheless, some 2,700 F-5 aircraft were built for the US and 30 other nations by the time production ceased in 1987. Perhaps the most well-known variant of the F-5 is the related T-38 Talon two-seat advanced trainer used by the US Air Force and NASA.
Data below for F-5E |
|
| HISTORY: | |
| First Flight |
(F-5A) 30 July 1959 (RF-5A) May 1968 (F-5E) 11 August 1972 (RF-5E) 29 January 1979 (F-5F) 25 September 1974 |
| Service Entry |
(F-5E) April 1973
|
| CREW: |
one: pilot
|
| ESTIMATED COST: |
(T-38) $756,000
|
| AIRFOIL SECTIONS: | |
| Wing Root | NACA 65A004.8 |
| Wing Tip |
NACA 64A004.8
|
| DIMENSIONS: | |
| Length | 47.38 ft (14.45 m) |
| Wingspan | 28.67 ft (8.13 m) |
| Height | 13.25 ft (4.06 m) |
| Wing Area | 186 ft² (17.2 m²) |
|
Canard Area
|
not applicable
|
| WEIGHTS: | |
| Empty | 9,723 lb (4,410 kg) |
| Normal Takeoff | unknown |
| Max Takeoff | 24,722 lb (11,214 kg) |
| Fuel Capacity |
internal: 2,541 L external: unknown |
|
Max Payload
|
(F-5) 7,000 lb (3,175 kg) (F-20) 8,000 lb (3,630 kg) |
| PROPULSION: | |
| Powerplant | two General Electric J85-21A afterburning turbojets |
| Thrust |
10,000 lb (44.48 kN)
|
| PERFORMANCE: | |
| Max Level Speed |
at altitude: 1,085 mph (1,745 km/h) at 36,000 ft
(10,975 m), Mach 1.64 at sea level: unknown |
| Initial Climb Rate | 34,500 ft (10,500 m) / min |
| Service Ceiling | 51,800 ft (15,790 m) |
| Range |
typical: 240 nm (445 km) ferry: 1,545 nm (2,865 km) |
| g-Limits |
unknown
|
| ARMAMENT: | |
| Gun | two 20-mm M39A2 cannons (280 rds ea) |
| Stations | five external hardpoints and two wingtip rails |
| Air-to-Air Missile | AIM-9 Sidewinder |
| Air-to-Surface Missile | AGM-65 Maverick |
| Bomb | Mk 82/83/84 GP, BLU-107 Durandal, CBU-52 cluster |
| Other |
ECM pods, rocket pods
|
| KNOWN VARIANTS: | |
| N-156F | Northrop model number by which the first F-5 prototype was designated; 3 built |
| F-5A | Production one-seat Freedom Fighter originally built without a radar but later upgraded with the APQ-153; 1,200 built |
| CF-5A | Freedom Fighter license built by Canadair in Canada, also equipped for reconnaissance duties; 89 built |
| F-5A (G) | Variant of the F-5A built for Norway |
| NF-5A | Freedom Fighter license built by Canadair for the Netherlands and Venezuela, also fitted with reconnaissance equipment; 75 built |
| RF-5A | Reconnaissance model based on the F-5A; 120 built |
| RF-5A (G) | Reconnaissance model based on the F-5A sold to Norway |
| SRF-5A | Reconnaissance model license built by CASA for Spain; 17 built |
| F-5B | Two-seat trainer |
| F-5C Skoshi Tiger | F-5A model modified with aerial refueling gear, updated electronics, and armor and used by the US Air Force for combat trials in Vietnam from October 1965 to May 1967; 17 built |
| F-5D | Proposed trainer model; not built |
| F-5E Tiger II | Improved variant intended to fulfill a need for a lightweight, low-cost fighter to be exported to US allies, included modifications to improve manueverability and STOL performance, increased fuel capacity, and improved fire-control using a more powerful radar; about 1,400 built |
|
F-5E Tiger III F-5F Tiger III |
Chilean Air Force F-5E/F fleet upgraded with an improved radar |
| RF-5E TigerEye | Reconnaissance model with advanced cameras and infrared scanners in an enlarged nose, purchased by Iran, Malaysia and Saudi Arabia; at least 12 built |
| RF-5E TigerGazer | Taiwan F-5E model modified for reconnaissance duties by Singapore; 7 converted |
| F-5F | Two-seat combat-capable trainer with a lengthened fuselage |
|
F-5G or F-20 Tigershark |
Advanced F-5 derivative with a F404 turbofan engine, increased payload, and much improved avionics; 3 prototypes built but did not enter production |
| F-5N | F-5E aircraft acquired by the US Navy and used for aggressor training |
| F-5S | Singapore variant of the F-5E updated with the Grifo-F X-band radar and equipped to operate the AMRAAM missile |
| F-5EM & F-5FM | Brazilian F-5E/F fleet modernized with the Grifo-F radar |
| F-5T | Modernized F-5F trainer used by Singapore |
| F-5T Tigris | Thai F-5E fleet modernized by Israel with an improved radar |
| F-5TIII | Designation for modernized F-5E fleet used by Morocco |
| T-38 |
Two-seat trainer based on the F-5A; 1,114 built for USAF
|
| KNOWN COMBAT RECORD: |
Vietnam War (USAF, South Vietnam, 1965-1975) Ogaden War (Ethiopia, 1977-1978) North-South Yemen conflict (Taiwan, 1979-1985) Polisario conflict (Morocco, 1979-1991) Iran-Iraq War (Iran, 1980-1988) Iraq - Operation Desert Storm (Saudi Arabia, 1991) |
| KNOWN OPERATORS: |
Austria, Östereichische Luftstreitkräfte (Austrian Air Force) Bahrain, Bahrain Amiri (Royal Bahraini Air Force) Botswana (Botswana Defence Force Air Arm) Brazil, Força Aérea Brasileira (Brazilian Air Force) Canada (Canadian Armed Forces, Air Command) Chile, Fuerza Aérea de Chile (Chilean Air Force) Ethiopia, Ye Ityopya Ayer Hayl (Ethiopian Air Force) Greece, Elliniki Polimiki Aeroporia (Hellenic Air Force) Honduras, Fuerza Aérea Hondureña (Honduran Air Force) Indonesia, Tentara Nasional Indonesia - Angkatan Udara (Indonesian Air Force) Iran (Imperial Iranian Air Force) Iran (Islamic Republic of Iran Air Force) Jordan, Al Quwwat al-Jawwiya al-Malakiya al-Urduniya (Royal Jordanian Air Force) Kenya (Kenya Air Force) Libya, Al Quwwat al Jawwiya al Jamahiriya al Arabia al Libyya (Libyan Air Force) Malaysia, Tentera Udara Diraja Malaysia (Royal Malaysian Air Force) Mexico, Fuerza Aérea Mexicana (Mexican Air Force) Morocco, Al Quwwat al Jawiyya al Malakiya Marakishiya (Royal Moroccan Air Force) Netherlands, Koninklijke Luchmacht (Royal Netherlands Air Force) Norway, Kongelige Norske Luftforsvaret (Royal Norwegian Air Force) Pakistan, Pakistan Fiza'ya (Pakistani Air Force) Paraguay, Fuerza Aérea Paraguaya (Paraguay Air Force) Philippines, Hukbong Himpapawid ng Pilipinas (Philippine Air Force) Saudi Arabia, Al Quwwat al Jawwiya al Malakiya as Sa'udiya (Royal Saudi Air Force) Singapore (Republic of Singapore Air Force) South Korea, Han-guk Kong Goon (Republic of Korea Air Force) Spain, Ejército del Aire Española (Spanish Air Force) Sudan, Silakh al Jawwiya As'Sudaniya (Sudanese Air Force) Switzerland, Schweizer Luftwaffe (Swiss Air Force) Taiwan, Chung-Kuo Kung Chuan (Republic of China Air Force) Thailand, Kongtap Agard Thai (Royal Thai Air Force) Tunisia, Al Quwwat al-Jawwiya al-Jamahiriyah At'Tunisia (Republic of Tunisia Air Force) Turkey, Türk Hava Kuvvetleri (Turkish Air Force) United States (US Air Force) United States (US Marine Corps) United States (US Navy) Venezuela, Fuerza Aérea Venezolana (Venezuelan Air Force) Vietnam, Khong Quan Nhan Dan Viet Nam (Vietnam People's Army Air Force) Yemen, Al Quwwat al Jawwiya al Yemeniya (Unified Yemen Air Force) |
|
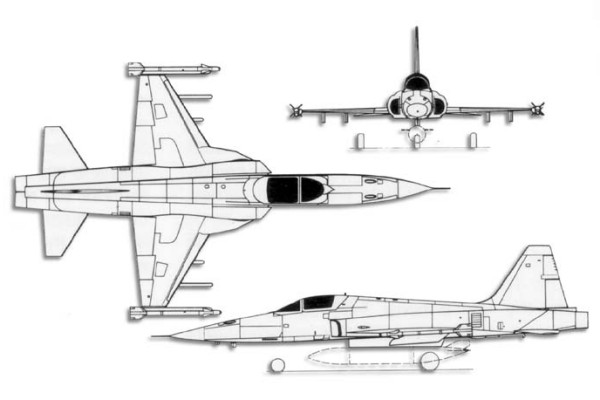
3-VIEW SCHEMATIC:

|
|
SOURCES:
|
|


|
Aircraft | Design | Ask Us | Shop | Search |

|
|
| About Us | Contact Us | Copyright © 1997- | |||
|
|
|||