|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
 - -
|
|

|
McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II Multi-Role Fighter |
|
DESCRIPTION:
The venerable Phantom design dates back to 1955 when the US Navy requested a fleet defense fighter with a powerful radar and armed only with air-to-air missiles. By the early 1960s, the Air Force realized that the Phantom, with its outstanding flight performance and payload, was superior to any of its own aircraft in use at the time. The Air Force purchased 583 F-4Cs little different from the Navy's F-4Bs and 773 F-4Ds with improved radar and ground attack capability. The Phantom saw considerable action in the Vietnam War where its lack of an onboard gun was found to be a considerable disadvantage. This was rectified in the F-4E, which also included more powerful engines and updated radar. The final US version of the Phantom was the F-4G 'Wild Weasel' defense suppression aircraft tasked with destroying enemy surface-to-air missiles (SAMs) and their radar. Including those for allied air forces, over 5,100 examples of the Phantom were built. The final US model in service, the F-4G 'Wild-Weasel' defense-suppression aircraft, was withdrawn in 1998. Those models still in service elsewhere are due for replacement soon.
Data below for F-4E |
|
| HISTORY: | |
| First Flight |
(XF4H-1) 27 May 1958 (F-4C) 27 May 1963 |
| Service Entry |
August 1962
|
| CREW: |
two: pilot, systems officer
|
| ESTIMATED COST: |
unknown
|
| AIRFOIL SECTIONS: | |
| Wing Root | NACA 0006.4-64 |
| Wing Tip |
NACA 0003-64
|
| DIMENSIONS: | |
| Length | 63.00 ft (19.20 m) |
| Wingspan | 38.62 ft (11.77 m) |
| Height | 16.46 ft (5.02 m) |
| Wing Area | 530 ft² (49.2 m²) |
|
Canard Area
|
not applicable
|
| WEIGHTS: | |
| Empty | 30,328 lb (13,757 kg) |
| Normal Takeoff | 41,490 lb (18,818 kg) [fighter mission] |
| Max Takeoff | 61,795 lb (28,030 kg) |
| Fuel Capacity |
internal: 7,022 L external: 5,070 L |
|
Max Payload
|
16,000 lb (7,257 kg)
|
| PROPULSION: | |
| Powerplant | two General Electric J79-17A afterburning turbojets |
| Thrust |
35,800 lb (159.2 kN) with afterburner
|
| PERFORMANCE: | |
| Max Level Speed |
at altitude: 1,430 mph (2,300 km/h) at 36,000 ft
(10,975 m), Mach 2.17 at sea level: 905 mph (1,450 km/h), Mach 1.19 |
| Initial Climb Rate | 28,000 ft (8,535 m ) / min |
| Service Ceiling | 58,750 ft (17,905 m) |
| Range |
typical: 1,720 nm (3,185 km) ferry: 2,000 nm (3,700 km) |
| g-Limits |
unknown
|
| ARMAMENT: | |
| Gun | one 20-mm M61A1 Vulcan cannon (640 rds) |
| Stations | seven external hardpoints |
| Air-to-Air Missile | AIM-120 AMRAAM, AIM-7 Sparrow, AIM-9 Sidewinder, Sky Flash |
| Air-to-Surface Missile | AGM-65 Maverick, AGM-88 HARM, AGM-12 Bullpup |
| Bomb | GBU-16 Paveway LGB, Mk 82/83/84 GP, cluster |
| Other |
ECM pods
|
| KNOWN VARIANTS: | |
| XF4H-1 | Prototype |
| F4H-1F or F-4A | First production fighter for US Navy; 45 built |
| F4H-1 or F-4B | Navy fighter model, first version built with intended engine installed; 649 built |
| EF-4B | 'B' model refitted for ECM training; 1 converted |
| NF-4B | 'B' model used for development testing; 1 converted |
| QF-4B | Former 'B' airframes used as target drones for testing supersonic missiles |
| RF-4B | Unarmed day/night reconnaissance aircraft based on F-4B but with longer nose holding cameras and IR sensors, used by US Marines; 46 built |
| F-110A or F-4C | Attack fighter for US Air Force; 635 built |
| EF-4C | 'C' airframes reconfigured for 'Wild Weasel' defense suppression mission |
| YRF-4C | F-4Bs converted into prototypes of reconnaissance aircraft for USAF; 2 converted |
| RF-4C | Production tactical reconnaissance model for USAF based on F-4C airframe but fitted with RF-4B equipment; 499 built |
| F-4D | Air Force model specifically tailored to USAF fighter and strike missions; 773 built (of which 68 later transferred to Iran and South Korea) |
| EF-4D | 'D' models converted to 'Wild Weasel' mission |
| YF-4E | YRF-4C airframe converted into prototype of F-4E; 1 converted |
| F-4E | Improved strike model with improved engines, increased fuel capacity, redesigned nose containing smaller radar, leading-edge slats, and first model equipped with 20-mm cannon; 1,405 built |
| F-4EJ | Japanese version of F-4E built under license by Mitsubishi and Kawasaki; 139 built |
| RF-4E | Reconnaissance model for export; 130 built |
| RF-4EJ | Japanese reconnaissance model; 14 built |
| F-4F | Air superiority fighter based on F-4E tailored for Germany; 175 built |
| F-4G | 'E' models converted to 'Wild Weasel' defense suppression mission for USAF |
| YF-4J | 'B' models converted into prototypes for F-4J; 3 converted |
| F-4J | Strike model for Navy/Marines with new engines, larger wing, and advanced avionics; 518 built |
| F-4K or FG.1 | British carrier-based model based on F-4J; 50 built |
| F-4M or FGR.2 | British Royal Air Force model; 116 built |
| F-4N | Navy/Marines 'B' models upgraded with new avionics and strengthened structure; 228 converted |
| QF-4N | 'N' models converted to target drones |
| F-4S | Navy/Marines 'J' models upgraded with stronger structure and leading-edge slats |
| Kurnass 2000 |
Israeli upgraded version
|
| KNOWN COMBAT RECORD: |
Vietnam War (USN, USMC, USAF, 1965-1972) War of Attrition (Israel, 1969-1970) Yom Kippur War (Israel, 1973) Iran-Iraq War (Iran, 1980-1988) Lebanon (Israel, 1982) shot down by Saudi Arabian F-15Cs (Iran, 1984) Iraq - Operation Desert Storm (USAF, 1991) Iraq - Operation Southern Watch (USAF, 1991-1998) |
| KNOWN OPERATORS: |
Australia (Royal Australian Air Force) Egypt, Al Quwwat al Jawwiya il Misriya (Egyptian Air Force) Germany, Deutsche Luftwaffe (German Air Force) Greece, Elliniki Polimiki Aeroporia (Hellenic Air Force) Iran (Imperial Iranian Air Force) Iran (Islamic Republic of Iran Air Force) Israel, Tsvah Haganah le Israel - Heyl Ha'Avir (Israeli Defence Force - Air Force) Japan, Nihon Koku-Jieitai (Japan Air Self Defence Force) South Korea, Han-guk Kong Goon (Republic of Korea Air Force) Spain, Ejército del Aire Española (Spanish Air Force) Turkey, Türk Hava Kuvvetleri (Turkish Air Force) United Kingdom (Royal Air Force) United States (US Air Force) United States (US Air National Guard) United States (US Marine Corps) United States (US Navy) United States (US Naval Reserve) United States (NASA) |
|
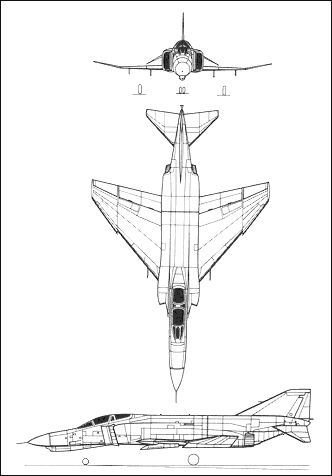
3-VIEW SCHEMATIC:
|
|
SOURCES:
|
|


|
Aircraft | Design | Ask Us | Shop | Search |

|
|
| About Us | Contact Us | Copyright © 1997- | |||
|
|
|||