|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
|
||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||
The designations used for most guided missiles, unguided rockets, and other self-propelled flying vehicles follow the general format illustrated below:
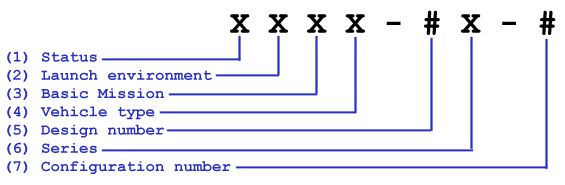
The purpose of these letters and numbers is further described in the following tables.
| Status Prefix | Launch Environment | Mission | Vehicle Type | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Captive | A | Air | C | Transport | B | Booster |
| D | Dummy | B | Multiple | D | Decoy | M | Guided Missile |
| J | Special Test (temporary) | C | Coffin | E | Electronic/ Communications | N | Probe |
| N | Special Test (permanent) | F | Individual | G | Surface Attack | R | Rocket |
| X | Experimental | G | Surface | I | Aerial/Space Intercept | S | Satellite |
| Y | Prototype | H | Silo Stored | L | Launch Detection/ Surveillance | ||
| Z | Planning | L | Silo Launched | M | Scientific/ Calibration | ||
| M | Mobile | N | Navigation | ||||
| P | Soft Pad | Q | Drone | ||||
| R | Ship | S | Space Support | ||||
| S | Space | T | Training | ||||
| U | Underwater | U | Underwater Attack | ||||
| W | Weather | ||||||
| Letter | Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| C | Captive | Vehicle that can be carried by a launch platform but cannot be fired, such as an air-launched missile that is not fitted with a rocket motor. These are often used during flight testing, for example. |
| D | Dummy | A dummy casing that carries no operational equipment (i.e. motor, warhead, guidance system). These may be used for training or aerodynamic flight tests. |
| J | Special Test (temporary) | Vehicle in special test programs with a special test configuration or with equipment temporarily removed to accommodate testing. |
| N | Special Test (permanent) | Vehicle in special test programs whose configuration changes so drastically that returning to its original operational configuration is not practical. |
| X | Experimental or Prototype | A weapon that is still under development or evaluation and not in production. |
| Y | Prototype or Preserial | Indicates that the weapon has moved beyond the experimental stage and is in final developmental testing and evaluation in preparation for a production run. |
| Z | Planned, Proposed, or Projected | A weapon that is still in early planning or pre-development stages. |
| Letter | Environment | Description |
|---|---|---|
| A | Air | Launched from an air vehicle. |
| B | Multiple | Capable of being launched from more than one environment. |
| C | Coffin or Container | Ground-launched system that is stored horizontally or at an angle less than 45° in a protective enclosure. |
| F | Individual or Infantry | A man-portable weapon that is carried and launched by combat personnel. |
| G | Surface | Launched from the ground or a runway. |
| H | Silo Stored | Stored vertically in a silo but not launched from underground. |
| L | Silo Launched | Vertically stored and launched from underground. |
| M | Mobile | Launched from a ground vehicle or moveable platform. |
| P | Softpad | Ground-launched system that is stored in an unprotected or partially-protected state. |
| R | Ship | Launched from a surface vessel. |
| S | Space | Launched from a vehicle operating outside the Earth's atmosphere. |
| U | Underwater | Launched from an underwater location or a submarine. |
| Letter | Mission | Description |
|---|---|---|
| C | Transport | Designed to carry personnel, cargo, command, control, and communications equipment or weapons systems. |
| D | Decoy | Designed or modified to confuse, deceive, or divert enemy defenses by simulating an attack vehicle. |
| E | Electronic Warfare or Special Electronic Equipment |
Designed or modified with electronics equipment for communications, countermeasures, electronic radiation sounding, or other electronic recording or relay missions. |
| G | Surface Attack | Intended to attack land or sea targets, such as ground structures and vehicles or surface ships. |
| I | Intercept, Aerial or Space | Intended to attack aerial targets, such as aircraft or missiles, or space targets, such as missiles or satellites. |
| L | Launch Detection/Surveillance | Performs aerospace surveillance to detect and track satellites or in-flight missiles. |
| M | Scientific/Calibration | Designed for the collection, evaluation, analysis, and interpretation of scientific and technical information. |
| N | Navigation | Provides navigational data. |
| Q | Drone or Target | Remotely or automatically piloted aerospace vehicle. |
| S | Space Support | Vehicle designed to ensure maintainability of space control and support of terrestrial forces. Includes activities such as launching and deploying space vehicles, maintaining and sustaining space vehicles while in orbit and recovering space vehicles if required. |
| T | Training | Designed or permanently modified for training purposes. |
| U | Underwater Attack | Intended to attack sub-surface targets such as submarines. |
| W | Weather | Observes, records, or relays data pertaining to meteorological phenomena. |
| Letter | Vehicle | Description |
|---|---|---|
| B | Booster | A primary or auxiliary propulsion system used as a source of thrust for a satellite, missile, or aerospace vehicle. May consist of one or more units. |
| M | Guided Missile or Drone | An unmanned, self-propelled vehicle flying in or above the atmosphere with remote or internal trajectory guidance. |
| N | Probe | A non-orbital instrumented vehicle used to monitor and transmit environmental information. |
| R | Rocket | A self-propelled unguided vehicle whose flight trajectory cannot be altered after launch. |
| S | Satellite | An orbital vehicle that collects and transmits data. |
(Status) Launch Mission Vehicle - Number Series - Config. number (Name)
R U R - 5 A Asroc
Ship Underwater Attack Rocket 5th rocket 1st variant
C A T M - 9 M - 8 Sidewinder
Captive Air Training Missile 9th missile 12th variant 8th subvariant
C I M - 10 B Bomarc
Coffin Intercept Missile 10th missile 2nd variant
G Q M - 15 A Regulus II
Runway Drone Missile 15th missile 1st variant
P T M - 16 E Atlas
Softpad Training Missile 16th missile 5th variant
A D M - 20 B Quail
Air Decoy Missile 20th missile 2nd variant
L G M - 25 C Titan II
Silo-launched Surface Attack Missile 25th missile 3rd variant
Y U G M - 27 A Polaris
Prototype Underwater Surface Attack Missile 27th missile 1st variant
X M G M - 52 B Sea Lance
Experimental Mobile Surface Attack Missile 52nd missile 2nd variant
B Q M - 74 E Chukar
Multiple Drone Missile 74th missile 5th variant
F I M - 92 A Stinger
Individual Intercept Missile 92nd missile 1st variant
A I M - 120 C - 7 AMRAAM
Air Intercept Missile 120th missile 3rd variant 7th subvariant
Z A I M - 132 A ASRAAM
Planned Air Intercept Missile 132nd missile 1st variant
P W N - 10 B Super Loki Datasonde
Softpad Weather Probe 10th probe 2nd variant
S B - 5 A Titan IV
Space Support Booster 5th booster 1st variant
N S - 7 E Navstar GPS IIF
Navigation Satellite 7th satellite 5th variant
You can test your knowledge of the Tri-Service naming conventions
at Andreas Gehrs-Pahl's list of
US Missiles & Rockets and
Andreas Parsch's
Current Designations of U.S.
Unmanned Military Aerospace Vehicles.
Related Topics:
What is the difference between a missile and a rocket or a bomb, a cluster bomb, and a guided bomb?
Read More Articles:


|
Aircraft | Design | Ask Us | Shop | Search |

|
|
| About Us | Contact Us | Copyright © 1997- | |||
|
|
|||